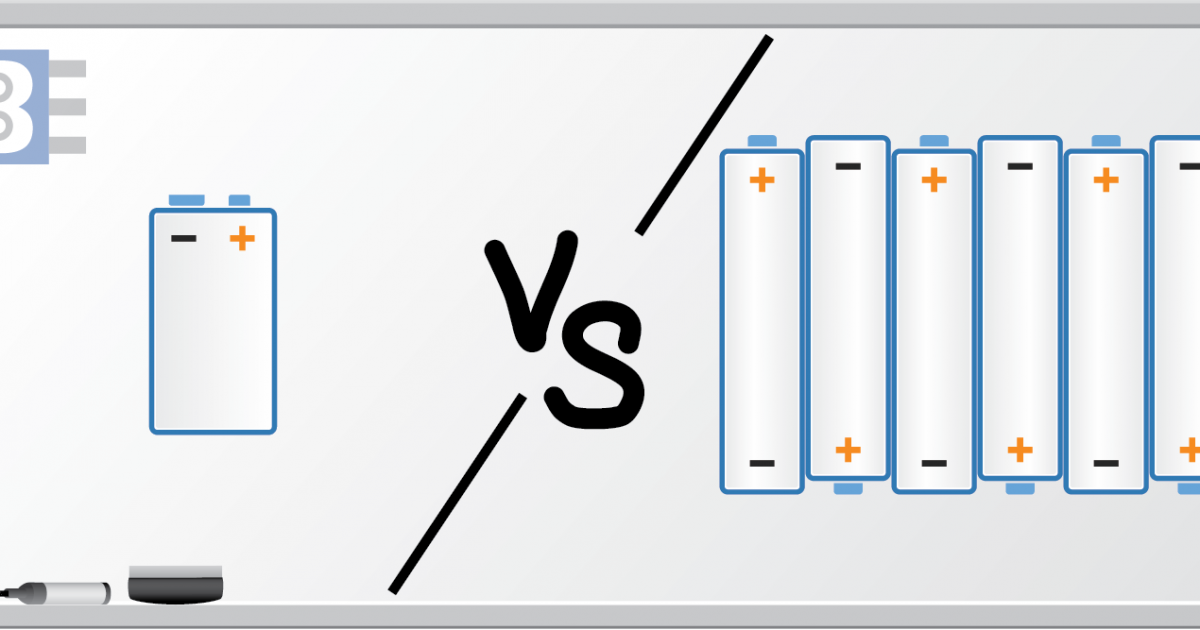
Three 1kω resistors are connected in parallel and powered by 9v battery. Unlike wiring batteries in series when batteries are wired in parallel the voltage does not increase the output voltage is the average voltage of all batteries in the circuit.
Analyzing A Resistor Circuit With Two Batteries Video
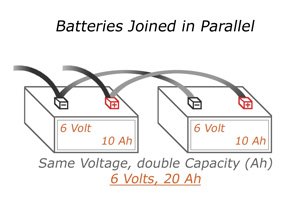
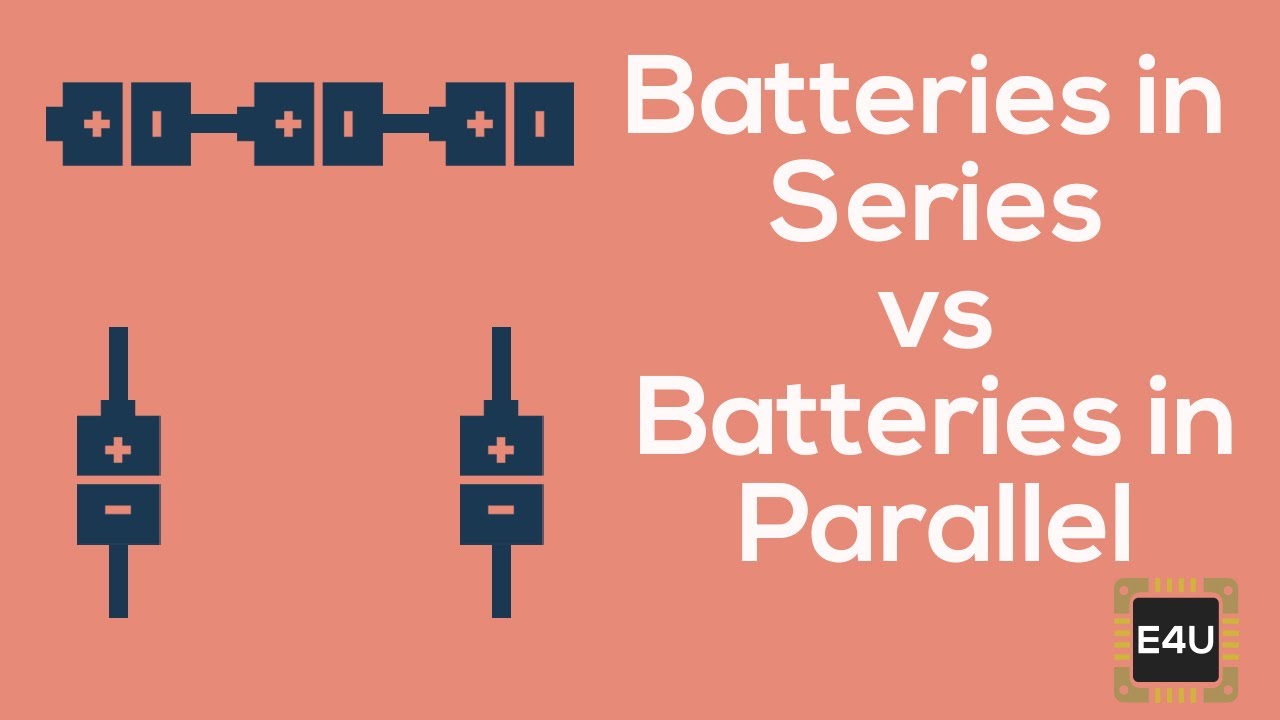
9v batteries in parallel. The basic concept is that when connecting in parallel you add the amp hour ratings of the batteries together but the voltage remains the same. For example if a 3v and a 9v battery were wired in parallel the output voltage would be 6v 93 divided by 2 however the current will be total amperage of all batteries in the circuit minus any losses. Hence when charging these batteries it is important to utilize a charger that satisfies the 12 volt capacity that is necessary for both the 6 volt batteries connected in series. In contrast batteries connected in a parallel configuration are able to increase the amp hour capacity of your batteries at the same voltage. When the resistor value gets change the current flow value also gets change. Two 6 volt 45 ah batteries wired in parallel are capable of providing 6 volt 9 amp hours 45 ah 45 ah.
The current flow varies in each node depends on the resistor value. Here total current is 27ma and the current flow through r1 is 9ma r2 is 9ma and r3 is 9ma. You will also be able to find some series parallel resistance practice problems on our page. Question 1 consider a circuit with a voltage of 9v and consisting of five resistors with a resistance of 30ω each. You can connect your load to one of the batteries and it will drain both equally. We will now look at some resistors in series and parallel problems and solutions.
Negative to negative and positive to positive. The 2nd config is 4 parallel connections at each battery end also 2 rows of 4 batteries each row connected in series and of course the 3rd image is 3 parallel connections with 3 batteries connected across their and terminals and a single row of serial connected batteries to make 48v. To join batteries in parallel use a jumper wire to connect both the positive terminals and another jumper wire to connect both the negative terminals of both batteries to each other. For more information on wiring in parallel see connecting batteries in parallel or our article on building battery banks. Connecting in series increases voltage only the basic concept when connecting in series is that you add the voltages of the batteries together but the amp hour capacity remains the same.